|
While our life expectancy has been extended with the marked advancement of medical science/practice and everybody can pursue their personal well-being, we are still living with anxiety and fear as well as courage and hope in the midst of new storms such as a more complicated social life, opportunistic infections, lifestyle-related diseases, and aging-related problems.
Nobody objects to prioritizing health. We consider that disease prevention is essential for staying healthy. From the standpoint of preventive medicine, we have been engaged in R&D activities, believing that new health-promoting products are only created in the course of basic research on the significance of microbial flora.
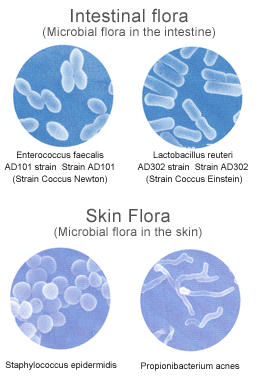
Regarding health maintenance/improvement, one of the effective methods to achieve this may be the utilization of useful bacteria that form microbial floras in the intestine, skin, mouth, and vagina. Today, it is an accepted fact that a total of 100 trillion good and bad bacteria in the intestine are closely related to our health. The point is to identify new useful bacteria from complicated intestinal floras, find substances that increase useful bacteria (or decrease bad bacteria), clarify the mechanisms of such substances, and determine how to commercialize them as products.
While experiencing some changes, we have been continuing research on the significance of microbial flora for more than two decades.
|
|
So far, we have conducted studies on the following improving and/or disease-preventing effects of the intestinal, skin oral floras on:
- Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis
- Hypertension
- Liver and kidney functions
- Infection control and immunity
- Caries and periodontitic disease
- Intestinal and skin floras
- Regulation of intestinal functions
- Adjustment of skin physiology
As study themes, the effects of microbial flora on a variety of lifestyle-related diseases and chronic disorders (obesity, hyperglycemia, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, intractable bowel diseases, collagen diseases, anomaly in hormonal secretion, etc.), diverse infections, and allergic diseases, as well as the mechanisms of those effects are too extensive to investigate without difficulty, suggesting the ever-increasing importance of research into microbial flora.
|
 |


